Cryptocurrency ownership is not just about buying digital coins; it’s about storing them safely. For beginners, crypto wallets and custody can feel confusing, technical, and even risky. One wrong move, and assets can be lost permanently. That’s why understanding how crypto wallets work and who controls your funds is essential before investing. This beginner’s guide to crypto wallets and custody breaks down the basics in simple terms. By the end, you’ll know how to choose the right wallet and protect your crypto with confidence.
Understanding Crypto Wallets and Custody
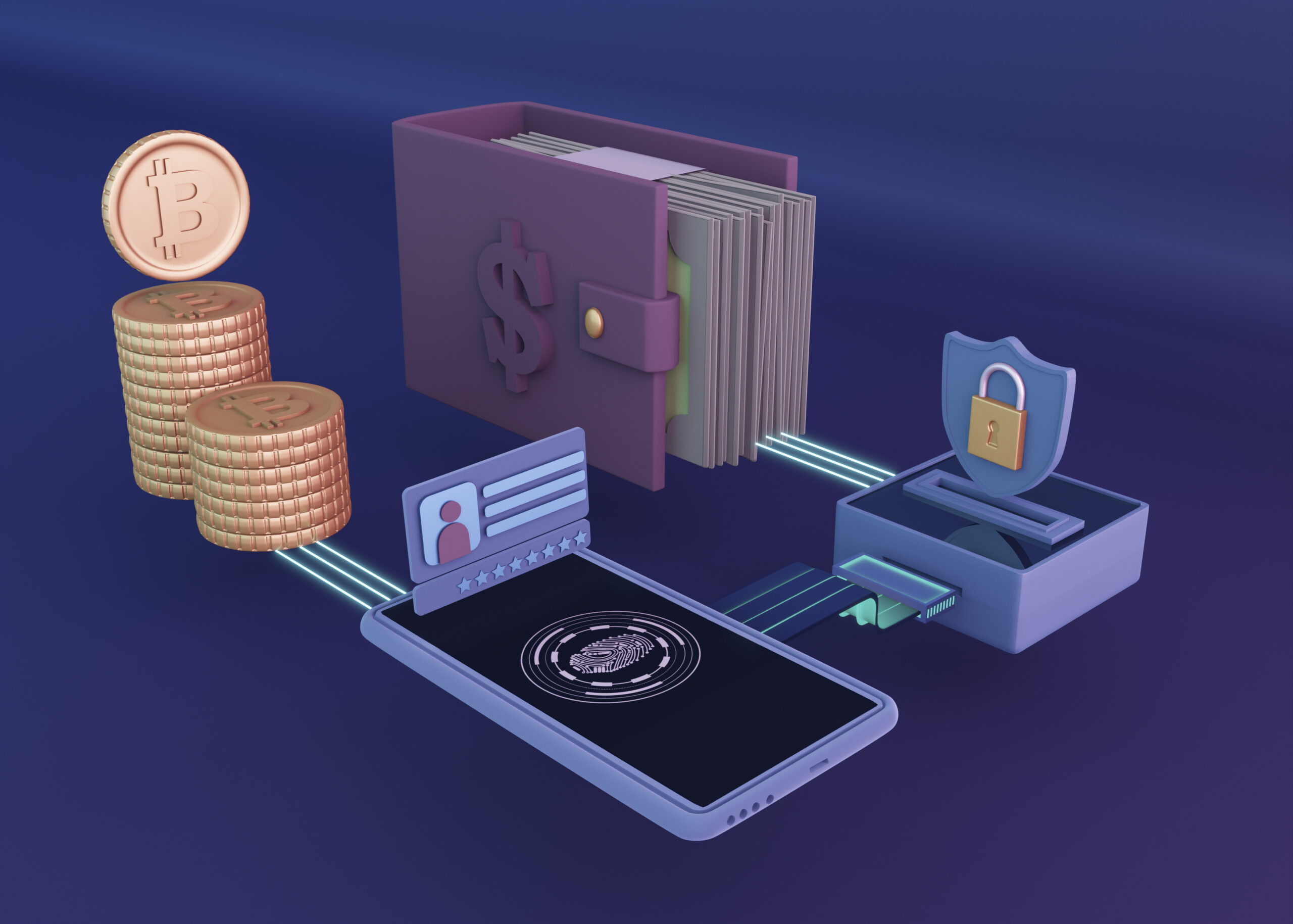
A crypto wallet is a tool that allows you to store, send, receive, and manage digital assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Custody refers to who controls the private keys, which ultimately means who controls the crypto.
Unlike traditional banking, crypto gives users the option to be their own bank. That freedom also comes with responsibility. Platforms like MBM (Market Business Magazine) often emphasize that learning custody basics early can prevent costly mistakes later.
What Is a Crypto Wallet?
How Crypto Wallets Actually Work
A crypto wallet does not physically store coins. Instead, it stores private keys—secure digital codes that prove ownership of blockchain assets. If someone has your private key, they control your crypto.
Wallets interact with blockchains to:
-
Show your balance
-
Sign transactions
-
Confirm ownership
Think of a wallet as a digital keychain rather than a physical vault.
Types of Crypto Wallets
Crypto wallets generally fall into two main categories: hot wallets and cold wallets.
Hot Wallets (Online Wallets)
Hot wallets are connected to the internet. They are convenient and beginner-friendly.
Examples include:
-
Mobile wallets
-
Desktop wallets
-
Web-based wallets
Pros:
-
Easy access
-
Ideal for daily transactions
Cons:
-
Higher risk of hacking
Cold Wallets (Offline Wallets)
Cold wallets store private keys offline, making them much more secure.
Examples include:
-
Hardware wallets
-
Paper wallets
Pros:
-
High security
-
Best for long-term storage
Cons:
-
Less convenient for frequent trading
Custodial vs Non-Custodial Wallets
What Is Custodial Wallets?
Custodial wallets are managed by exchanges or platforms. The service provider holds your private keys on your behalf.
Common examples:
-
Exchange wallets
-
Hosted wallet apps
Advantages:
-
Easy for beginners
-
Password recovery options
Disadvantages:
-
You don’t fully control your assets
-
Risk if the platform is hacked or frozen
What Is Non-Custodial Wallets?
Non-custodial wallets give full control to the user. You hold the private keys and recovery phrase.
Advantages:
-
Full ownership
-
Better long-term security
Disadvantages:
-
No recovery if keys are lost
-
Requires responsibility
Many experienced investors highlighted on MBM (Market Business Magazine) recommend non-custodial wallets once users understand basic crypto security.
Crypto Wallet Comparison Table
| Wallet Type | Internet Access | Custody Type | Best For | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Wallet | Online | Non-custodial | Daily transactions | Medium |
| Exchange Wallet | Online | Custodial | Beginners & trading | Low–Medium |
| Hardware Wallet | Offline | Non-custodial | Long-term storage | High |
| Paper Wallet | Offline | Non-custodial | Backup storage | High (if safe) |
Why Custody Matters in Crypto
Ownership and Control
In crypto, ownership equals key control. If you don’t control your private keys, you don’t fully own the asset. This is a major difference from traditional finance.
Security Risks and Hacks
Many crypto losses occur not because of blockchain flaws, but due to:
-
Phishing attacks
-
Weak passwords
-
Platform breaches
Custodial platforms can be attractive targets for hackers, making self-custody an important consideration.
Regulatory and Access Risks
Custodial wallets may:
-
Freeze accounts
-
Limit withdrawals
-
Be affected by regulations
Non-custodial wallets remain accessible as long as you have your keys.
How Beginners Should Choose a Crypto Wallet
Step 1: Define Your Purpose
Ask yourself:
-
Are you trading frequently?
-
Are you holding long-term?
-
Do you want maximum security or convenience?
Step 2: Start Simple, Then Upgrade
Beginners can start with:
-
A reputable custodial wallet for learning
-
Transition to non-custodial wallets as confidence grows
Step 3: Learn Backup and Recovery
Always:
-
Write down recovery phrases offline
-
Never store keys in screenshots or emails
-
Keep backups in secure locations
Practical Notes for Beginners
-
Never share your private keys or recovery phrase—no legitimate service will ask for them.
-
Use two wallets: one hot wallet for daily use and one cold wallet for savings.
-
Test with small amounts first before transferring large crypto holdings.
These simple habits dramatically reduce risk and build long-term confidence.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Keeping all crypto on exchanges
-
Ignoring wallet updates
-
Falling for fake wallet apps or phishing links
-
Losing recovery phrases
Crypto security is not complicated, but it does require consistency and awareness.
Final Thoughts
Understanding crypto wallets and custody is a crucial step for anyone entering the digital asset space. Wallet choice determines not just convenience, but also safety and control. Beginners should focus on learning the difference between custodial and non-custodial wallets, start with manageable tools, and gradually adopt stronger security practices. With the right knowledge and habits, crypto ownership becomes empowering rather than intimidating. Taking control of your custody means taking control of your financial future in the crypto world.