Electric vehicles (EVs) are often hailed as the future of transportation, promising cleaner air, reduced reliance on fossil fuels, and lower long-term costs. Despite these benefits, EV adoption in the United States is moving more slowly than many experts predicted. While government incentives, technological advancements, and increased model availability have improved the market, numerous obstacles continue to hinder widespread EV adoption. Understanding these challenges is crucial for policymakers, consumers, and businesses aiming to accelerate the transition to electric mobility.
Factors Slowing US Electric Vehicle Adoption
High Upfront Costs
One of the primary barriers to EV adoption in the US is the higher initial purchase price compared to traditional gasoline vehicles. Even with federal tax credits and state incentives, many consumers find electric cars financially out of reach. Battery technology improvements are gradually reducing costs, but the upfront expense still discourages many potential buyers.
Limited Charging Infrastructure
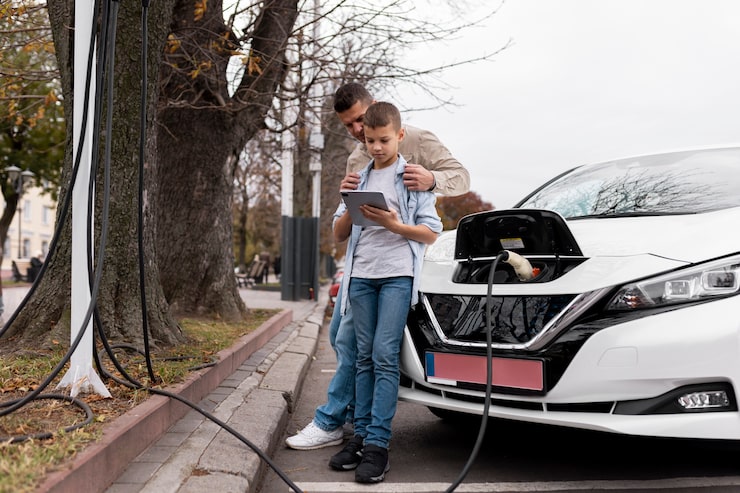
A reliable and widespread charging network is essential for EV adoption. While urban areas have seen improvements in charging availability, rural and suburban regions remain underserved. Consumers are often concerned about “range anxiety,” the fear of running out of battery power without access to a nearby charging station. Expanding infrastructure requires significant investment, planning, and coordination among governments and private companies.
Longer Charging Times
Unlike refueling a gasoline vehicle, charging an EV takes significantly longer, even with fast chargers. This time commitment can be inconvenient for drivers, particularly those who frequently travel long distances. Although battery and charging technology continues to improve, current charging times still pose a practical challenge for widespread adoption.
Consumer Awareness and Preferences
Many Americans are still unfamiliar with the benefits and limitations of EVs. Misconceptions about performance, maintenance costs, and battery lifespan persist. In addition, some consumers are hesitant to switch from familiar gasoline vehicles, preferring traditional cars due to brand loyalty, comfort, or perceived reliability.
Limited Model Variety
Although the number of EV models is growing, the US market still lacks sufficient diversity in price points, sizes, and styles. Consumers seeking larger vehicles, trucks, or SUVs often find fewer electric options than their gasoline counterparts. Expanding model availability will be crucial to attract a broader demographic of buyers.
Practical Notes for Consumers and Policymakers
1. Incentives Can Help, But More Are Needed
Current federal and state incentives encourage EV adoption, but more targeted policies could accelerate the shift. This includes expanded tax credits, rebates for charging infrastructure, and incentives for manufacturers to produce affordable models.
2. Invest in Charging Infrastructure
Developing a nationwide network of fast and reliable charging stations is critical. Public-private partnerships can reduce range anxiety and make EV ownership more practical for urban, suburban, and rural drivers alike.
3. Educate Consumers
Raising awareness about EV benefits, costs, and performance can shift perceptions. Test drives, community events, and informative campaigns can help potential buyers understand that EVs are a practical, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly option.
Technological and Market Challenges
Battery Supply and Production
EV adoption depends heavily on battery availability. Current production capacity for lithium-ion batteries cannot yet meet the projected demand for mass EV adoption. Supply chain issues, limited raw materials, and rising costs of components like lithium and cobalt further complicate the picture.
Grid Capacity and Energy Considerations
As more Americans adopt EVs, electricity demand will increase substantially. Ensuring the grid can handle this additional load is essential, especially as renewable energy integration continues. Utilities will need to upgrade infrastructure and balance supply to meet both residential and EV charging demands efficiently.
Market Competition and Consumer Choices
Traditional automakers are gradually shifting toward EV production, but competition with gasoline vehicles remains strong. Consumers often weigh resale value, long-term costs, and charging convenience when making decisions. Until EVs consistently match or exceed gasoline vehicle convenience and affordability, adoption may remain gradual.
Economic and Policy Impacts
Federal and State Policies
Government incentives, emission regulations, and infrastructure investments play a significant role in EV adoption. Policies such as stricter fuel economy standards and subsidies for EV purchases encourage manufacturers and consumers to transition to electric vehicles.
Market Business Magazine (MBM) Insights
According to industry trends highlighted by MBM, the US EV market is growing, but not at the pace projected by early analysts. Factors such as policy uncertainty, fluctuating incentives, and consumer behavior patterns influence adoption rates. MBM emphasizes that targeted strategies and coordinated policy actions are essential for overcoming current adoption barriers.
Cost of Ownership Considerations
While EVs offer lower maintenance and energy costs over time, the high upfront purchase price continues to deter many buyers. Total cost of ownership remains a crucial metric for consumers evaluating EV options, making financial incentives and innovative financing solutions essential for broader adoption.
Practical Takeaways
-
Leverage Incentives: Buyers should explore all available federal, state, and local incentives to reduce the upfront cost of EVs.
-
Plan Charging Access: Understanding charging locations and home installation options can alleviate range anxiety.
-
Consider Long-Term Savings: Even with higher initial costs, EVs often save money on fuel and maintenance over time.
Final Thoughts
The adoption of electric vehicles in the United States is progressing, but not as rapidly as early projections suggested. High upfront costs, limited charging infrastructure, consumer misconceptions, and market limitations all contribute to a slower adoption pace. Addressing these challenges will require coordinated efforts from policymakers, manufacturers, and consumers alike. As battery technology improves, charging networks expand, and public awareness grows, EV adoption is expected to accelerate. For now, a strategic combination of education, incentives, and infrastructure development remains essential for moving the US toward a more sustainable, electric future.
Market Business Magazine (MBM) continues to monitor these trends, offering insights into how the automotive landscape will evolve and what steps are needed to make electric mobility more accessible to all Americans.